Diagnosing Vehicle Speed Sensor Symptoms and Solutions
Introduction
Vehicle speed sensors (VSS) play an essential role in modern automotive systems, providing crucial data for the functioning of the engine control unit (ECU), anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and transmission control systems. When a speed sensor malfunctions, it can lead to a cascade of issues affecting performance, safety, and efficiency. This article explores common symptoms of a failing vehicle speed sensor and offers practical solutions for diagnosis and repair.
The vehicle speed sensor is a critical component affecting numerous systems such as transmission, ABS, and engine management.

In this article we will discuss some of the explores common symptoms of a failing vehicle speed sensor and offers practical solutions for diagnosis and repair.
Table of Contents
Understanding Vehicle Speed Sensors
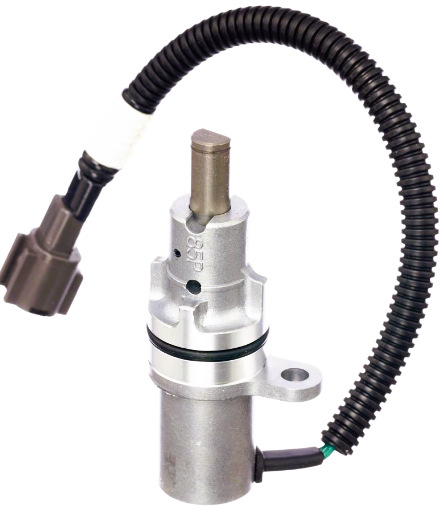
Before delving into symptoms and solutions, it is important to grasp the fundamental operation of vehicle speed sensors. Typically mounted on the transmission or wheel hubs, these sensors are responsible for sending rotational speed data to various control units within the vehicle. This data is critical for determining gear shifting points, optimal fuel injection, and ensuring the proper functioning of safety systems such as ABS.
Common Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Vehicle Speed Sensor
1. Erratic Speedometer Readings:
Symptom: This is often the most noticeable sign of a faulty VSS. You might experience a speedometer that jumps erratically or ceases to work entirely.
Cause: A failing sensor cannot consistently send accurate data to the vehicle’s ECU, leading to inaccurate speed readings.
2. Transmission Shifting Problems:
Symptom: Delays in gear shifts, abrupt shifting, or transmission being stuck in a single gear.
Cause: Since the transmission relies on accurate speed data to determine optimal shifting points, a malfunctioning sensor disrupts these calculations, leading to performance issues.
3. Illuminated Check Engine Light:
Symptom: The check engine light may illuminate if the ECU detects erroneous or absent data from the speed sensor.
Cause: Fault codes specific to VSS failures are stored in the vehicle’s computer system, often due to short circuits or a complete loss of functionality in the sensor.
4.Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Malfunction:
Symptom: An ABS warning light might appear on the dashboard, indicating a problem.
Cause: The ABS relies on wheel speed data to modulate braking force. A compromised sensor can affect this function, reducing braking efficiency and safety.
5. Reduced Cruise Control Functionality:
Symptom: Difficulty in maintaining a stable cruise control speed or cruise control completely disengaging.
Cause: Inadequate speed input disrupts the cruise control system, which depends on precise speed readings to maintain set speed levels.
6. Increased Fuel Consumption:
Symptom: Noticeable drop in fuel efficiency.
Cause: Engine management systems rely on speed data for optimal fuel injection timing. A faulty sensor can lead to inefficient fuel use, increasing consumption.
7. Engine Performance Issues:
Symptom: Instances of engine stalling or hesitation during acceleration.
Cause: Inaccurate speed signals can impact engine management, leading to improper air-fuel mixture ratios and engine response issues.
Diagnosing Vehicle Speed Sensor Problems

Diagnosing speed sensor issues involves a combination of manual inspection and electronic diagnostics. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Visual Inspection:
Check for any visible damage or corrosion around the sensor and its wiring. Loose connections or broken wires can result in intermittent or total signal loss.
2. Scan for Trouble Codes:
Use an OBD-II scanner to identify any fault codes. Common codes related to VSS malfunction include P0500 (Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction) and similar variants, which provide a good starting point for troubleshooting.
3. Testing the Sensor:
Utilize a multimeter to check the resistance and output voltage of the speed sensor. Compare these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure they are within acceptable ranges.
4. Inspect the Speedometer Cable:
In older vehicles, an issue might be related to a mechanical speedometer cable. Inspect for wear and tear or kinks in the cable that could impact speed data transmission.
Solutions for Vehicle Speed Sensor Problems
Once a failing sensor has been identified, addressing these issues involves several possible solutions:
1.Repair Connections and Wiring:
If the problem lies in faulty wiring or loose connections, repair or replace the damaged parts. Ensuring tight and corrosion-free connections is crucial for optimal signal transmission.
2. Clean the Sensor:
In some cases, dirt and debris can block the sensor operation, especially for sensors located in wheel hubs. Carefully cleaning the sensor might solve the problem without needing further intervention.
3. Replace the Sensor:
If the sensor is deemed defective through diagnostic tests, replacement is often the most effective solution. Ensure that the replacement sensor is identical to the original in terms of specifications and mounting style.
4. Re-calibrate the System:
Post-replacement, some vehicles require a system re-calibration to ensure that the ECU correctly interprets the new sensor signals. This process might necessitate specialized equipment or procedures available at professional repair centers.
5. Check Related Systems:
If transmission or ABS systems show continued issues after sensor replacement, inspect related components such as torque converters or wheel hubs for underlying problems.
Preventive Measures
To avoid future issues with speed sensors, consider these preventive maintenance tips:
1. Regular Inspection:
Incorporate sensor and wiring inspections into routine maintenance schedules. Early detection of wear can prevent sensor failures.
2. Keep Components Clean:
Regularly clean the areas where sensors are mounted to prevent dirt buildup, which could interfere with sensor operation.
3. Use Quality Parts:
When replacing sensors or related components, opt for high-quality parts that meet OEM specifications. This investment can ensure longevity and better performance.
4. Avoid DIY Fixes for Complex Problems:
While basic diagnostic and replacement tasks can be done by enthusiasts, complex electronic issues should be addressed by professionals to avoid exacerbating the problem.
Conclusion
The vehicle speed sensor is a critical component affecting numerous systems such as transmission, ABS, and engine management. Understanding the symptoms of a malfunctioning sensor and employing effective solutions ensures optimal vehicle performance and safety. By combining diagnostic skills with preventive maintenance, vehicle owners can significantly reduce the risk of sensor-related issues, maintaining both efficiency and the driving experience. As automotive technology continues to evolve, staying informed about these components becomes increasingly important, allowing for better handling of potential challenges on the road.
1. How can I diagnose a Vehicle Speed Sensor problem?
Answer:
Visual Inspection: Check for visible damage or corrosion on the sensor and wiring.
OBD-II Scanner: Use this tool to identify any fault codes related to the sensor.
Multimeter Testing: Measure the resistance and output voltage of the sensor and compare it to specification standards.
Inspect the Speedometer Cable: In older cars, check the cable for wear and tear.
2. How does a faulty Vehicle Speed Sensor affect transmission?
Answer:
A faulty VSS can send erroneous speed data, leading to incorrect shifting patterns, delayed shifts, or the transmission getting stuck in a certain gear. This happens because the transmission control module relies on accurate speed information for optimal performance.
3. Can a faulty VSS cause the ABS warning light to turn on?
Answer:
Yes, since the ABS system uses data from speed sensors to prevent wheel lock-up during braking, a malfunctioning VSS can trigger the ABS warning light, indicating reduced braking efficiency.
4. Why is my car consuming more fuel when the VSS is faulty?
Answer:
The VSS provides data essential for determining the correct fuel injection and ignition timing. A malfunctioning sensor can disrupt these functions, leading to inefficient fuel use and increased consumption.
5. How can I fix a faulty Vehicle Speed Sensor?
Answer:
Repair Connections: Fix any loose or corroded connections or wires.
Clean the Sensor: Remove any dirt or debris obstructing the sensor.
Replace the Sensor: If the sensor is defective, replace it with one matching OEM specifications.
Re-calibrate Systems: After replacement, some vehicles may require recalibration of their systems to recognize the new sensor.






